Difference between revisions of "EEG"
Caseorganic (Talk | contribs) |
Caseorganic (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
===Definition=== | ===Definition=== | ||
| − | Electroencephalography | + | Electroencephalography, or EEG, is a method of monitoring electrical activity produced the firing of neurons in the brain. Information from the brain is generally collected by attaching electrodes to the scalp and a grounder attached to the ear. The first Electroencephalograph was taken by [[Hans Berger]] in 1924.<ref>David Millet (2002), "The Origins of EEG" International Society for the History of the Neurosciences (ISHN).</ref> |
===EEG Concerts=== | ===EEG Concerts=== | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<blockquote><youtube size="medium" align="left" wrap="yes">Ff-Dmlreg4I</youtube></blockquote> | <blockquote><youtube size="medium" align="left" wrap="yes">Ff-Dmlreg4I</youtube></blockquote> | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Brain Controlled Activities=== | ||
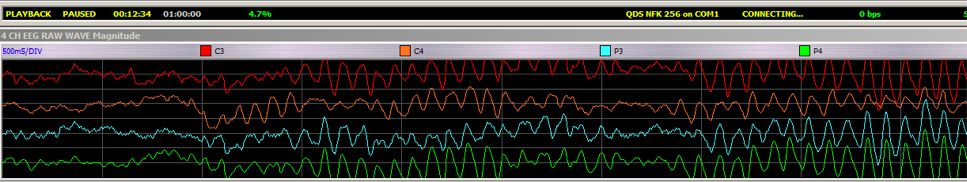
| + | Numerous games and other systems can be controlled through electrodes attached to the scalp. One notable experiment by Derek Zumbach is a way of receiving feedback during meditation by detecting detached synchronous alpha brain activity.<ref>E-mail from EEG and Alpha synchrony researcher Derek Zumbach to Kyle Drake and Amber Case on May 18, 2012.</ref> Alpha synchrony is a measure of the focus element during peak performance. The system detects alpha waves, which are 1/10th of a second in length and are one of two brainwave patterns that occur in a multi-synchronous manner. Using the Bio Explorer software, Derek can see alpha synchrony as well as standard resting cortical activity. | ||
| + | [[image:alpha-synchrony-shown-in-red-derek-zumbach.jpg|750px|left]] | ||
| + | An screenshot of a person's real-time performance while doing a 60-minute meditation session. The event of alpha synchrony is red and standard resting cortical activity in blue. Synchronous alpha activity is one of the most flagrant cortical patterns one can encounter while reading an EEG.<ref>E-mail from EEG and Alpha synchrony researcher Derek Zumbach to Kyle Drake and Amber Case on May 18, 2012.</ref> | ||
===Related Reading=== | ===Related Reading=== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 23: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| + | [[Category:Marked for Editing]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Book Pages]] | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
Revision as of 21:23, 18 May 2012
Definition
Electroencephalography, or EEG, is a method of monitoring electrical activity produced the firing of neurons in the brain. Information from the brain is generally collected by attaching electrodes to the scalp and a grounder attached to the ear. The first Electroencephalograph was taken by Hans Berger in 1924.[1]
EEG Concerts
On August 30, 2003, James Fung, Ph.D. held a brainwave music concert, where a computer sensed audience reaction to regenerate and alter to music on the fly, reacting to their responses to the music.
"Audience members became part of an advanced mass EEG system which used audience brainwaves to control both the music and lighting environment....the mood of the environment (was) "regenerated" by the collective consciousness of the attendees" [2].
Brain Controlled Activities
Numerous games and other systems can be controlled through electrodes attached to the scalp. One notable experiment by Derek Zumbach is a way of receiving feedback during meditation by detecting detached synchronous alpha brain activity.[3] Alpha synchrony is a measure of the focus element during peak performance. The system detects alpha waves, which are 1/10th of a second in length and are one of two brainwave patterns that occur in a multi-synchronous manner. Using the Bio Explorer software, Derek can see alpha synchrony as well as standard resting cortical activity.
An screenshot of a person's real-time performance while doing a 60-minute meditation session. The event of alpha synchrony is red and standard resting cortical activity in blue. Synchronous alpha activity is one of the most flagrant cortical patterns one can encounter while reading an EEG.[4]
Related Reading
References
- Jump up ↑ David Millet (2002), "The Origins of EEG" International Society for the History of the Neurosciences (ISHN).
- Jump up ↑ REGEN3 / Regenerative Brainwave Music: ElectroBrainFunk
- Jump up ↑ E-mail from EEG and Alpha synchrony researcher Derek Zumbach to Kyle Drake and Amber Case on May 18, 2012.
- Jump up ↑ E-mail from EEG and Alpha synchrony researcher Derek Zumbach to Kyle Drake and Amber Case on May 18, 2012.